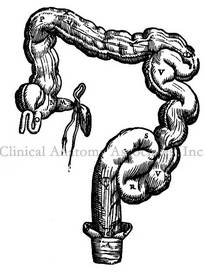
The rectum is the most distal segment of the large intestine, along with the anal canal.
The word [rectum] arises from the Latin [rectus] and means "straight", such as its use in the name "rectus abdominis" for the "straight muscle of the abdomen".
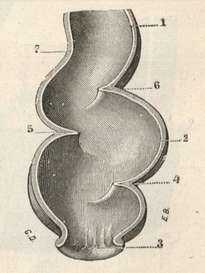
It seems a misnomer, as the rectum of the human species is actually "S" shaped, as seen in the accompanying image. The reason for this discrepancy is that the rectum was named by Galen of Pergamon (129AD - 200 AD) who himself studied this structure in animals such as sheep and goats. In these animals the rectum is indeed straight, and since contradicting Galen was not acceptable (see Michael Servetus), the name has survived until this day. Even Andreas Vesalius has in his 1953 "Fabrica" a depiction of a straight rectum in the human! Click on second image to see a larger depiction of Vesalius' idea of the rectum. Although Vesalius stated that he wanted to show human anatomy as it is, and not as Galen said it should be, here is a demonstration that in 1543 he was still a lukewarm Galenist.
There is an area between the sigmoid and the rectum called the sigmoidorectal junction, although most anatomists call it (wrongly) the rectosigmoid junction (RSJ). This is an anatomically diffuse area with no clear anatomical transition between the sigmoid and the rectum or the RSJ from the rectum.
As the proximal end of the "S" shaped rectum is not clearly discernible from the sigmoidorectal region, there is no clear agreement on the length of the rectum. Authors state that it measures approximately six to seven inches in length (15 - 17 cm), while others measure it as between 8-10 inches. The rectum ends distally at the junction of the rectum with the pelvic diaphragm. It is at this point that the anal canal begins.
The rectum is characterized by three transverse rectal folds, one on the right side, and two on the left side. These folds are know as the "rectal valves" or the "valves of Houston". The middle rectal fold is known to European anatomists as the "valve of Kohlrausch" Their function in maintaining fecal material in place as well as their function in defecation is still under study. The rectal valves also have a high level of anatomical variation and may not be present at all.
Images:
1. "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8 Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
2. "De Humani Corporis Fabrica, Libri Septem" A. Vesalius 1543 Brussels
Recommended reading: "Transverse Folds of Rectum: Anatomic Study and Clinical Implications" Shafik, A, et al. Clin Anat 14: 196-203 (2001).