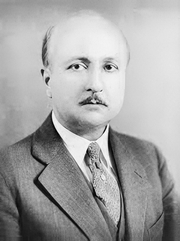This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.

Jean-Francois Calot (1861 – 1944)
Jean-Francois Calot (1861 – 1944). French physician and anatomist, Jean-Francois Calot was born in Arrens-Marsous, a small farming community of the Hautes-Pyrénées. He received his bachelor degree in 1880 at Saint-Pe de Bigorre, and then continued to study Medicine at the University of Paris, where he worked as an anatomy prosector. His doctoral thesis “De La Cholecystectomie” (On Cholecystectomy) was published in 1890 and republished in 1891.
Although his main interest laid in orthopedics and tuberculosis, Calot’s name is eponymically tied to an anatomical landmark described in his thesis, the “Triangle of Calot”, a triangular area that includes the biliary ducts associated with the gallbladder and the vascular supply to the gallbladder. This is an important region because of the high number of anatomical variations found in the area.
There is a discrepancy between the original description of this triangular region by Calot and what is used today. For more information, click on this link to read more on the “Triangle of Calot”, also known as the “cystohepatic triangle”.
During his medical career Calot worked at several French hospitals including the Rothschild hospital where he became Chief of Surgery. He was also the Chief of Surgery for the Cazin-Perrochaud Hospital, and the Orthopedic Institute of Berck-sur-Mer
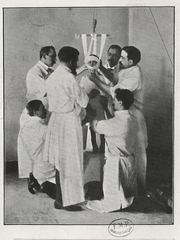
Dr. Jean-Francois Calot and
the treatment of Pott's disease
During his orthopedic career Calot published many books “Chirurgie et orthopédie de guerre”, “Les maladies qu'on soigne á Berck”, “Berck et ses traitements : les raisons de sa supériorit?”, but his opus magnus is the book “« L'orthopédie indispensable aux praticiens” (Indispensable orthopedics for practitioners).
Calot is also known for his treatment of tuberculotic abscesses, and a conservative approach to musculoskeletal tuberculosis. The surgical approach of the times was to surgically open and clean the tuberculotic bone. Calot is known to have said “Ouvrir la tuberculose, c'est ouvrir la porte d' la mort” (To open the tuberculosis is to open the door to death).
Continuing his studies and treatment of tuberculosis, on December 22nd, 1896 Calot presents the the French Academy of Medicine a study of the treatment of 37 patients with hyperkyphosis due to Pott’s disease, a tuberculotic spinal deformity, named after Sir Percival Pott. This method included traction and a brace. The second image shows this treatment. Dr. Calot is standing at the center, looking at the patient.
In 1900 Calot founded the “Orthopedic Institute of Berck” which today is known as “Calot’s Institute of Berck-sur-Mer”.
Sources:
1. “Calot's triangle” Abdalla S, Pierre S, Ellis H. Clin Anat. 2013 May;26 (4):493-501
2. “La Vie et l'OEuvre de Francois Calot, chirurgien orthopédiste de Berck” Loisel, P. (in French). Report presented at Société Francaise d'Histoire de la Médecine on 18 March 1987
Image 1: Original image courtesy of the National Library of Medicine
Image 2: Original image public domain courtesy of the Universite Paris-Descartes Histoire de la Santé