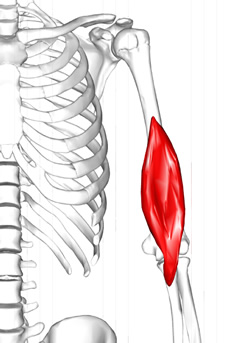
Brachialis muscle.
Click on the image for a larger depiction
UPDATED: The brachialis muscle is a skeletal muscle attached proximally to the anterior surface of the humerus and distally to the coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna. It is one of the three muscles in the anterior compartment of the arm (flexor compartment), the other two being the biceps brachii and the coracobrachialis.
It is a strong flexor of the elbow found deep to the biceps brachii. Because it does not attach to the radius, the brachialis muscle does not participate in the pronation and supination of the forearm.
The brachialis is supplied by branches of the brachial artery and by the recurrent radial artery.
The innervation of the brachialis muscle is a point to be discussed. Most modern books of anatomy state that this muscle is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6, and C7). Older and more detailed books state that this muscle has a dual innervation. A 2011 research paper published in Spanish (see Sources #6) describes this dual innervation. The proximal portion of the muscles is indeed innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, but the distal portion (in 90% of the cases) is innervated by muscular branches that arise off the radial nerve. The radial nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1) is a branch of the brachial plexus.
Following is an excerpt from the "Trail Guide to the Body" by Andrew Biel: "Ironically, (because it is deep to the biceps) the brachialis girth only helps the biceps brachii to bulge further from the arm, making the brachialis the biceps' "best friend"
Personal note: The research paper that describes the double innervation of the brachialis muscle was done at my alma mater, the University of Chile, and the authors' listing includes two of the contributors to this blog, Professors Claudio Molina and Cristian Uribe. Dr. Miranda
Sources:
1. “Gray’s Anatomy” Henry Gray, 1918
2. "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8th Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
3. "Gray's Anatomy" 42nd British Ed. Churchill Livingstone 2021
4. “An Illustrated Atlas of the Skeletal Muscles” Bowden, B. 4th Ed. Morton Publishing. 2015
5. "Trail Guide to The Body" 4th. Ed. Biel, A. Books of Discovery. 2010
6. "Doble Innervacion del Musculo Brachial en la Poblacion Chilena" Claudio Molina; Cristián Uribe; Álvaro Heras; Cristián Astorga;Jorge Lemus & Alberto Rodríguez. Int. J. Morphol, 2011. 29(4):1207-1211. A PDF copy of this paper is available here.
Note: The side image modified from the original by Anatomography, CC BY-SA 2.1 JP <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.1/jp/deed.en>, via Wikimedia Commons following Creative Commons attributes.