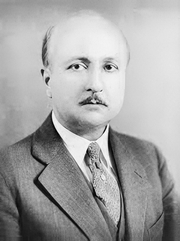This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.
Johannes Veslingius Mindanus (1598 – 1649). German surgeon, anatomist, botanist, and pharmacologist. Johann Vesling (mostly known by his Latinized name “Johannes Veslingius”) was born in a catholic family in Minden, Westphalia. He studied medicine in Leyden and Bologna. He later moved to the Venice medical college, where he became a professor of Anatomy in 1627. Veslingius had an interest in botany, which he pursued his whole life. Although German-born, Veslingius did most of his work and career in Italy.
In 1628 he traveled to Egypt and Jerusalem as a personal physician of Alvise Cornaro, the Venetian consul in Cairo. In 1632 he became a professor of anatomy and surgery at the University of Padua, in Italy, forcing his return from Jerusalem. At Padua, Veslingius became part of the long list of anatomists that followed Andreas Vesalius’ position.
Veslingius was the first to describe the arterial circle of the brain, eponymically tied today to Thomas Willis, and he was the first to name the soleus muscle, as it resembles the sole fish. In his words: “soleus, a figura piscis denominatus” translated “soleus, named for its fish shape”. Apparently, he was also the first to describe the pancreatic duct which lead to controversy with Wirsung. Veslingius was also the first to describe the four pulmonary veins, described as four of the great vessels.
Veslingius published his most important work, “Syntagma Anatomicum, publicis dissectionibus in auditorum usum diligenter aptatum”, in 1641. This work, which originally had no images, was republished in 1647 with full images in copper plates. This original work is important as it leaves the Vesalian tradition of posing the anatomical images with backgrounds and landscapes, dedicating the image solely to the anatomical information; in fact this is the first book to publish original images not copied or inspired from Vesalius’ Fabrica. This book was the first to influence Japanese anatomy.
Incredibly, Veslingius was accused of murdering Johan Georg Wirsung (1589 - 1643) with whom he had academic conflicts. Veslingius was acquitted of the accusation, and the name of Wirsung is today eponymously attached to the pancreatic duct.
The accompanying image is from the “Syntagma Anatomicum” and shows Veslingius with the following Latin words around him: “Ioannes Veslingius Mindanus Eques Hieros In Patauino Gymnasio Anatom. et Phar. Profess. Primarius” translated as: Johannes Veslingius Mindanus, Knight of Jerusalem, Primary Professor of Anatomy and Pharmacology of the School of Padua.
Below the image you can read: “Talis Apollinea floret Veslingius Arte. Purpureus nives pectore fulget Honor”, translated as: Veslingius flourishes by the art of Apollo who honors him by shining purple snow on his chest. Click on the image for a larger depiction and to see the Latin text.
Personal note: I am proud to have in my library catalog one of Veslingius’ original prints: “Tavole Anatomiche del Veslingio – Spiegate in Lingua Italiana” (Anatomical images from Veslingius, written in Italian), published in 1745 by Giovanni Battista Conzatti. Dr. Miranda
Original image courtesy of NLM. The title page of Syntagma Anatomicum courtesy of archive.org. Both images are in the public domain.
Sources:
1. “The Fabric of the Body. European Tradition of Anatomical Illustration” Roberts KB, Tomlinson JDW (1992) Oxford: Clarendon.
2. “The evolution of anatomical illustration and wax modelling in Italy from the 16th to early 19th centuries” Riva, A. et al. J. Anat. (2010) 216, 209–222
3. “The Anatomical School of Padua” Porzionato, A. et al. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012 Jun; 295(6):902-16
4. “The Origin of Medical Terms” Skinner, HA. 1970
5. "Johann Vesling (1598–1649):Seventeenth Century Anatomist of Padua and His Syntagma Anatomicum" SK Ghosh J Clin Anat 2014
Original image courtesy of the National Library of Medicine. The title page of Syntagma Anatomicum courtesy of archive.org. Both images are in the public domain.