UPDATED: There is no doubt that the book “De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem” written by Andreas Vesalius and published by Johannes Oporinus in May, 1543 is one of the most important scientific anatomical and medical books ever written. Much has been said about the place this book has in medical history as part of the discarding of dogmas and the establishment of scientific observation and thinking.
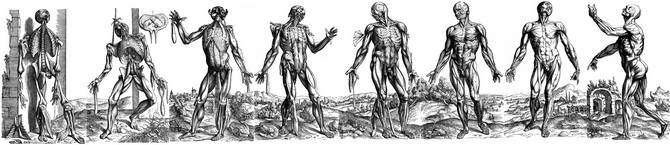
Some of the most intriguing images published in the book are fourteen woodcuts in the second book. These amazing and detailed images show the muscles in a whole body as it is dissected. The text details the structures and the procedure of how the dissection is performed.
It is believed that these images were done by Jan Stephan Van Calcar, an artist from the Titian’s studio, although there are indications that these images may have been authored by somebody else, or even that they were the effort of more than one artist working under the close supervision of Andreas Vesalius.
Today’s anatomical images are very descriptive and the artistry is relegated to the technique used for the depiction of the image. In Vesalius’ muscle men plates each image has a background showing a landscape. It was not until 1903 that it was discovered that the landscapes of the different images were part of a complete landscape. This is evident if these images are placed side by side. There have been several books and articles published on these images. Interestingly, some of the images had to be reversed to be placed in the panorama. This is due to the process of cutting the woodblocks.
The image in this article is one of two identified and composed by Harvey Cushing in 1943 (see sources). He calls it the "eight-series". The "six-series" can be seen here. To see Cushing's original template click here. The panorama of the six-series was identified by Cushing to be an area of the Euganean hills near Venice and Padua, Italy. There landscape formed by the eight-series is an actual region near Padua, Italy showing the ruins of old Roman baths. Cavanagh (1938) adds more information on these images, for his .pdf article, click here.
The image shown at the top of this article was created using original images from Vesalius’ Fabrica and composed using Adobe Fireworks CS5. Click on the image for a larger depiction. The large image is 1800px wide.
NOTE: In June 2023, I was able to purchase a single leaf of the 1543 Fabrica, page 187, which depicts one of the "muscle men". In the panorama image in this article it is figure number 3, from left to right. For more information on this image click here. This image is now properly framed in my office. Dr. Miranda.
This article continues here: "The landscape panorama of Vesalius' Muscle Men (2)"
Sources:
1. “A New View of the Vesalian Landscape” Cavanagh, GST Med Hist 1983, 27: 77-79
2. “The Panorama of Vesalius: A 'Lost' Design From Titian's Studio” Skandalakis, JE JAMA May 28, 1997, Vol 277, No. 20
3. “A Drawing for the Fabrica; and some Thoughts Upon the Vesalius Muscle-Men” Kemp. M. Med Hist. Jul 1970; 14(3): 277–288
4. “Andreas Vesalius: The Making, the Madman and the Myth” Joffe, SN. Persona Publishing 2009
5. "A Bio-Bibliography of Andreas Vesalius" Cushing, H. (1943) Schumann's