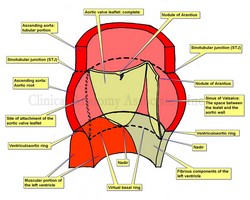
Aortic root and aortic valve.
Click for a larger image.
The term “aortic valve” refers to the three leaflets (or cusps) components that allow passage of blood from the left ventricle to the ascending aorta during ventricular systole, while at the same time preventing regurgitation or reflux of blood back into the ventricle during ventricular diastole. In reality, the “valve” is only a component of a larger structure called the “aortic root”. This article will describe the components of the aortic root and the aortic valve.
The ascending aorta presents with two distinct segments. The proximal segment is a dilated portion called the aortic root. The distal portion is known as the tubular portion of the ascending aorta. The boundary between these two portions is the [sinotubular junction (STJ). Some authors will recognize as the ascending aorta only the tubular portion.
The aortic root is that portion of the ventricular outflow tract and proximal aorta that supports the leaflets of the aortic valve. It is a functioning unit with relations both to the to the aorta and to the left ventricle, and it is here where in most cases we find the ostia of the right and left coronary arteries.
The aortic root is composed of the three dilated sinuses of Valsalva, two of which give origin to the coronary arteries (right and left), three leaflets (or cusps), and the interleaflet triangles. While the distal boundary of the aortic root is clearly defined (the STJ), the proximal boundary is not as clear and is difficult to define. The STJ is defined by the apices of the three aortic leaflets as well as a clear line that appears as the aorta passes from the dilations of the sinuses of Valsalva to the well-defined tubular portion of the ascending aorta.
This proximal boundary is defined clinically by two circular regions: the ventriculoaortic ring distally and the virtual basal ring proximally.
The ventriculoaortic ring is a circular region formed by the left ventriculoaortic junction (the point where the aorta anchors on the left ventricle), and fibrous tissue of both the “cardiac skeleton” and the membranous interventricular septum. It is also called the “surgical anulus”. This is the area where a surgeon will anchor an aortic replacement valve.
Continued here: The Aortic Root and the Aortic Valve (2)
Note: The image depicts only one complete aortic leaflet. The other one has been transected to show the sinus of Valsalva and the third has been removed to show the attachment or "hinge" of the leaflet. For an anatomical image of the aortic valve click here.
Sources:
1. The Anatomy of the Aortic Root: Loukas, M et al. Clinical Anatomy 27:748–756 (2014)
2. “Extracardiac aneurysm of the interleaflet triangle above the aortic-mitral curtain due to infective endocarditis of the bicuspid aortic valve.” Hori D, et al. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008 Aug;56(8):424-6
3. “Anatomy of the aortic root: implications for valve-sparing surgery” Efstratios I. Charitos, HS. Ann Cardiothorac Surg 2013;2(1):53-56
4. “The Forgotten Interleaflet Triangles: A Review of the Surgical Anatomy of the Aortic Valve” Sutton JP, et al Ann Thorac Surg 1995;59:419-27
Image property of: CAA, Inc. Artist: Dr. Miranda