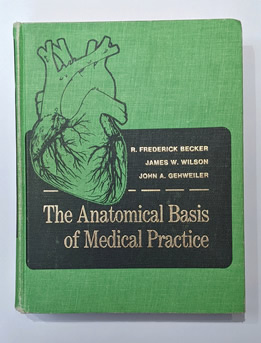
The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice - Book Cover
Click on the image for a larger version
The title of this article paraphrases the title of a paper authored by Edward Halperin, MD, MA., and published in “Academic Medicine,” the Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges in February 2009. More information in the "Sources" section of this article. I have also used other sources to complete this "strange tale."
"The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice" was published in 1971 by Williams & Wilkins. A large and heavy book, it is one of the many anatomy books written for medical students. This one however, stirred a controversy because of the "tongue-in-cheek" writing style of the authors and mostly because of the photographs of female nude models in seductive poses pretending to depict surface anatomy. The pictures were taken by a famous photographer, Peter Gowland.
Initial reviews were positive, as stated in the British Journal of Surgery, where the book is praised saying: "one only wishes that such a book was available when one was a student in the dissecting room."
Other reviews were more negative, as Dr. Edward A. Edwards in 1972 states: "...I feel compelled to say that the numerous photographs of comely young women, while enticing, no not well demonstrate the muscles and bony points the legends suggest as their purpose." He also says: "The book is marred by a waggishness expressed in facetiousness and in long digressions...."
Soon negative reactions to the book took place, many of them from anatomy professors who saw the illustrations as "out of place" and "not needed". Interestingly only a small percentage of the total images were of the "Playboy" style, while the rest of the images, photographs and sketches are of high educational quality.
Estelle R. Ramey, Emeritus Professor of Physiology and Biophysics at the Georgetown University School of Medicine, in a letter to the Association of Women in Science stated “In effect, the entire book is a calculated insult to women and men alike. It demeans the whole profession of medicine and is openly contemptuous of middle-aged women whose breasts are not so round and may even be rotting with cancer.” The AWIS as a whole threatened to boycott Williams and Wilkins Publishing, and as a result, the book was pulled off the market.
The story gets more interesting. Because of public pressure, angry letters to the publisher, and boycotts, the publisher agreed to stop all promotion, marketing, and sales of the book. Many assumed that they pulled the book off the market when, apparently because of low sales, they just let the initial run sell out by December 1972 and never republished it.
I do agree that the book transgresses the lines of decorum and respect for women that exist today. At the time of its publication the feminine movement was starting, and I think the authors tried (and failed) to have a humorous approach to what is at best, a difficult subject.
The book itself is a great book on anatomy and superficial anatomy, notwithstanding the images and comments. Since it was published and because of its scarcity, it has become a rare book, and as Dr. Halperin states “a minor collector’s item.” When published, this book sold for US$23.00. In 2009, at the time Dr. Halperin published his paper, the book was valued between US$ 89.00 and US$ 300.00; today (2025,) the book is valued between US$ 575.00 and US$1,000.00 in Abebooks.com.
"The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice" by Becker, R; Frederick; Wilson, James W; and Gehweiler, John, A. is one of the many books in my library and it has become known as “the green book” among my colleagues because of its bright green cloth hardcover. The image in this article is from the book in my library.
Sources:
1. “The Pornographic Anatomy Book? The Curious Tale of The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice" Halperin, E. Academic Medicine: February 2009 - Volume 84 - Issue 2 - p 278-283
2. "The anatomical basis of medical practice." By R. Frederick Becker, Ph.D., James W. Wilson, Ph.D., M.D., and John A. Gehweiler, M.D. 11 × 8¼ in. Pp. 907 + xv. Illustrated. 1971. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
3: "Five centuries of gender bias in anatomy" Elisabeth Brander — December 9, 2021
4. " The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice (NSFW)" September 10th, 2012
5. "The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice" by Becker, R; Frederick; Wilson, James W; and Gehweiler, John, A. 1971. The Williams & Wilkins Company
6. "The Anatomical Basis of Medical Practice" Book Review by Edwards, E. Ach. Surg. 1972