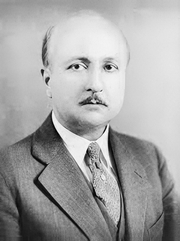This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.

Folder of "Sutures in Ancient Surgery"
During a recent 2024 lecture I delivered to a group of engineers at Medtronic, I met with Jack Kennedy, an engineer, past student, and a good friend. Jack and I share a passion for medical history. He has a very interesting collection of antique sutures and books related to the topic. He gifted me a collection of antique photographic prints in a leather-like folder with gilded letters. The name of the work is “Sutures in Ancient Surgery”. Jack was kind enough to sign and dedicate this gift that now holds an important place in my library.
For those who know me, I cannot have a book without looking into its history. What I found was incredible! The findings are in the following areas and topics:
- The history of the Davis and Geck suture company.
2. Lejaren à Hillier, main photographer of “Sutures in Ancient Surgery”
3. The content of the publication, images, and controversy
4. Missing prints
1. The history of the Davis & Geck company
Davis & Geck (D&G) was founded in 1909 by Charles T. Davis and Fred A. Geck, along with Frank D. Bradeen, and Benjamin F. Hirsch. Interestingly, Fred Geck left the company only a few months after its formation, but the company kept his name.
Located in Brooklyn, NY., the company specialized in the development and manufacture of surgical sutures along with various other medical products. Over the years the company changed ownership and has changed its name a couple of times. In 1930, the company was acquired by American Cyanamid after a trial between Charles Davis and his wife. This particular spot in the company’s history includes a murder, prison, lovers, and a trial. If you are interested, read the story of the company at UConn’s and SNAC web pages (see “sources”).
D&G was acquired by Sherwood, and later by the Tyco Corporation where it was renamed Syneture. Tyco Healthcare became Covidien, Ltd., which was later acquired by Medtronic, where it is today.
In 1970 Davis & Geck introduced Dexon, the first synthetic absorbable suture, followed shortly by Ethicon (J&J) sutures with Vicryl. Since then, research and development in the Medtronic line of sutures makes this company one of the world leaders in wound closure.
2. Lejaren à Hillier, main photographer of “Sutures in Ancient Surgery”
Lejaren à Hillier (1880-1969), was born in Milwaukee. He studied at the School of the Chicago Art Institute; his interest was classical fine arts. His studies and activities drew him to experimenting with photography and novel techniques for the times, where he mixed photography and painting. He became a famous commercial photographer.
One of his most exciting works was that of “tableaux vivants” (living portraits), where he would stage actors and innovative lighting techniques to represent scenes that he would later edit with paintings or use different photographic development techniques to obtain the appropriate mood. His work soon caught the attention of companies that used these tableaux vivants in commercial printings for brochures or newspapers.
Hillier was approached by D&G and the project of “Sutures in Ancient Surgery” was born. Starting in 1927 and all trough 1950, D&G sales representatives would present their customers (physicians and surgeons) with the “latest” image, ensuring an open door when they showed up at the doctor’s office. The doctors were also presented with a leather-like folder to maintain their collection. The number of prints varied each year, and it is interesting to note that none were published during the long years of WWII.
According to JTH Connor, a total of eighty three portraits were published. These show medical scenes that range from prehistory, trough Egypt, Greece, Rome, the Middle Ages, the Renaissance, all the way to the 19th century. The list of individuals portrayed is itself worth of research, as all of them in one way or another influenced medicine and surgery. Albucasis, Avicenna, Celsus, Fallopius, Fabricius, Galen, Harvey, Hunter, Rhazes, and Vesalius are but some of the tableaux vivants created for D&G.
Hillier was criticized for the lack of accuracy in some of the portraits as well as the person depicted, but the ideas for the topics were not his. The consultant used by D&G to suggest the topics was Samuel Harvey (1886-1953), who himself studied under the tutelage of famous neurosurgeon and medical historian Harvey Cushing (1869-1939).
Some of the images were later published in a book by Hillier (“Surgery through the ages”, 1944) showing other tableaux made for other medical publications.
This article continues here: The interesting story of “Sutures in Ancient Surgery (2)"